Research conducted recently and published in the journal Medicine showed that something amazing happens when you put intense mental effort into thinking or imaging you are lifting or moving with maximal exertion. Muscular strength can increase substantially and can match gains in strength made through more traditional intensive resistance training. What researchers discovered was that:
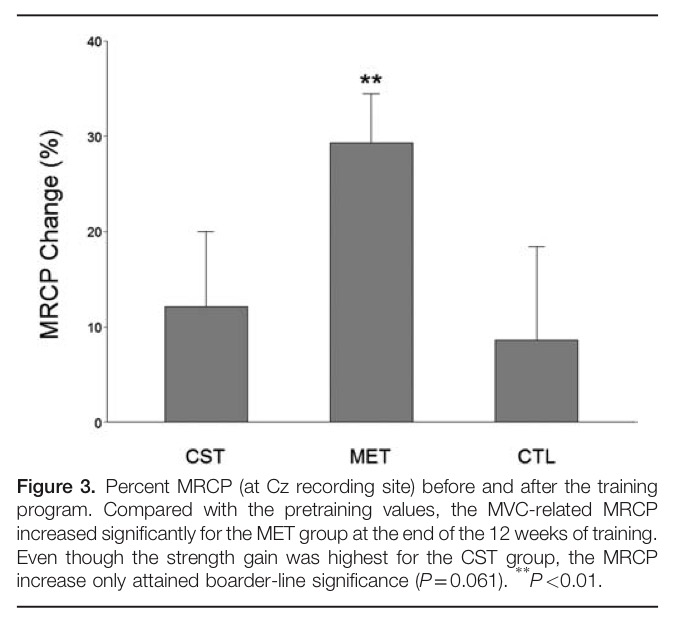
“strength of elbow flexor muscles, a frequently used large upper extremity muscle group during daily living, can be significantly improved by training of high motor effort combined with low-intensity muscle contraction in older adults, and the strength increase accompanied central signal augmentation that suggests an enhancement of descending command that was thought to have improved motor unit recruitment and activation leading to greater force production without changes in muscle morphology.”
Simple put, the strength of the elbow flexors – or colloquially known as “your guns” – were substantially increased in older adults after flexing the right elbow joint at minimal force whilst simultaneously mentally urging the forearm to pull upwards maximally. This type of ‘exercise’ is known as motor effort training or MET.

Trial summary: Training involved contracting the arm flexors at 30% of maximal effort while at the same time mentally urging the forearm to pull upward (elbow flexion) maximally for 5 seconds followed by 5 second of rest; this was repeated 25 times. Following a 2 minute rest this was repeated again. Training lasted for 12 weeks with 5 training session per week. This training protocol was compared to traditional strength training where participants performed 50 trials of isometric right elbow flexion at 80% of maximum force for 5 seconds in each training session; 60 session were completed. Training sessions, trials and trial duration were the same between groups. The intensity of the traditional strength training group was adjusted every 2 weeks based on subjects’ newer maximum strength attained as participants adapted to the training.
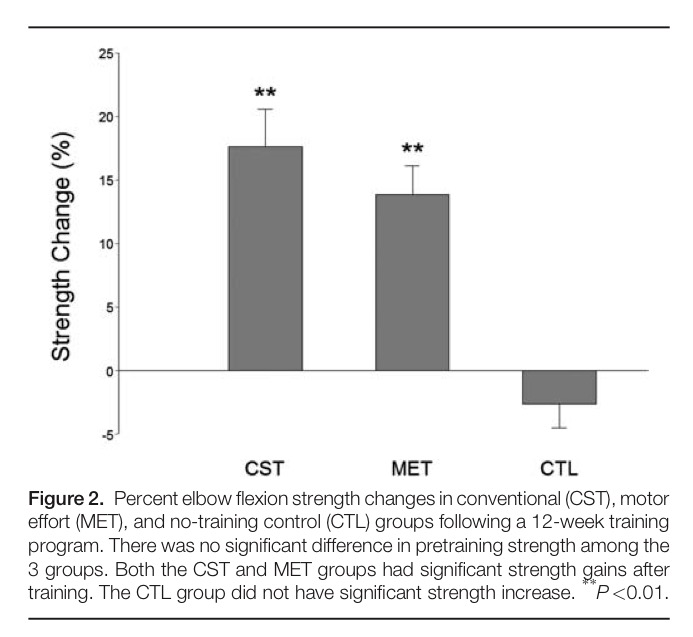
The current study is the first to show MET-induced strength gains in older adults with the improvements achieved statistically non-significant to traditional strength training. Strength improvements attained via MET appear to be modulated by an enhanced capacity to generate neurological drive from the motor cortex that then increases recruitment of motor units. What is particularly attractive about MET for older weak or frail adults is that it reduces problems and the risk of injury associated with performing conventional high-intensity strength training.
The authors conclude:
“The finding that the difference in strength increases between the MET and CST (traditional strength training) groups was statistically insignificant argues that training of motor imagery combined with low-intensity muscle exercise is a safe and effective method for muscle strengthening for vulnerable populations such as frail older individuals.”
For local Townsville residents interested in FitGreyStrong’s Exercise Physiology services or exercise programs designed to improve health, physical function and quality of life or to enhance athletic performance, contact FitGreyStrong@outlook.com or phone 0499 846 955 for a confidential discussion.
For other Australian residents or oversees readers interested in our services, please see here.
Disclaimer: All contents of the FitGreyStrong website/blog are provided for information and education purposes only. Those interested in making changes to their exercise, lifestyle, dietary, supplement or medication regimens should consult a relevantly qualified and competent health care professional. Those who decide to apply or implement any of the information, advice, and/or recommendations on this website do so knowingly and at their own risk. The owner and any contributors to this site accept no responsibility or liability whatsoever for any harm caused, real or imagined, from the use or distribution of information found at FitGreyStrong. Please leave this site immediately if you, the reader, find any of these conditions not acceptable.